According to the World Health Organization, more than 280 million people worldwide suffer from depression, a major mental health disease. People’s quality of life suffers from depression, which results in a loss of happiness and commitment to activities.
Depression is a complex mental health condition that might manifest differently in each individual. Common symptoms of depression include:
- Tiredness
- Sleeping disorders
- Eating disorders
- Aches on different locations of the body and more.
In this article, we will provide detailed information about the symptoms of depression. We will also explore other conditions that may mimic depression’s signs and offer guidance on medical treatment options. Additionally, we will provide actionable habits and practices that can aid in combating depression.
10 Common Symptoms of Depression
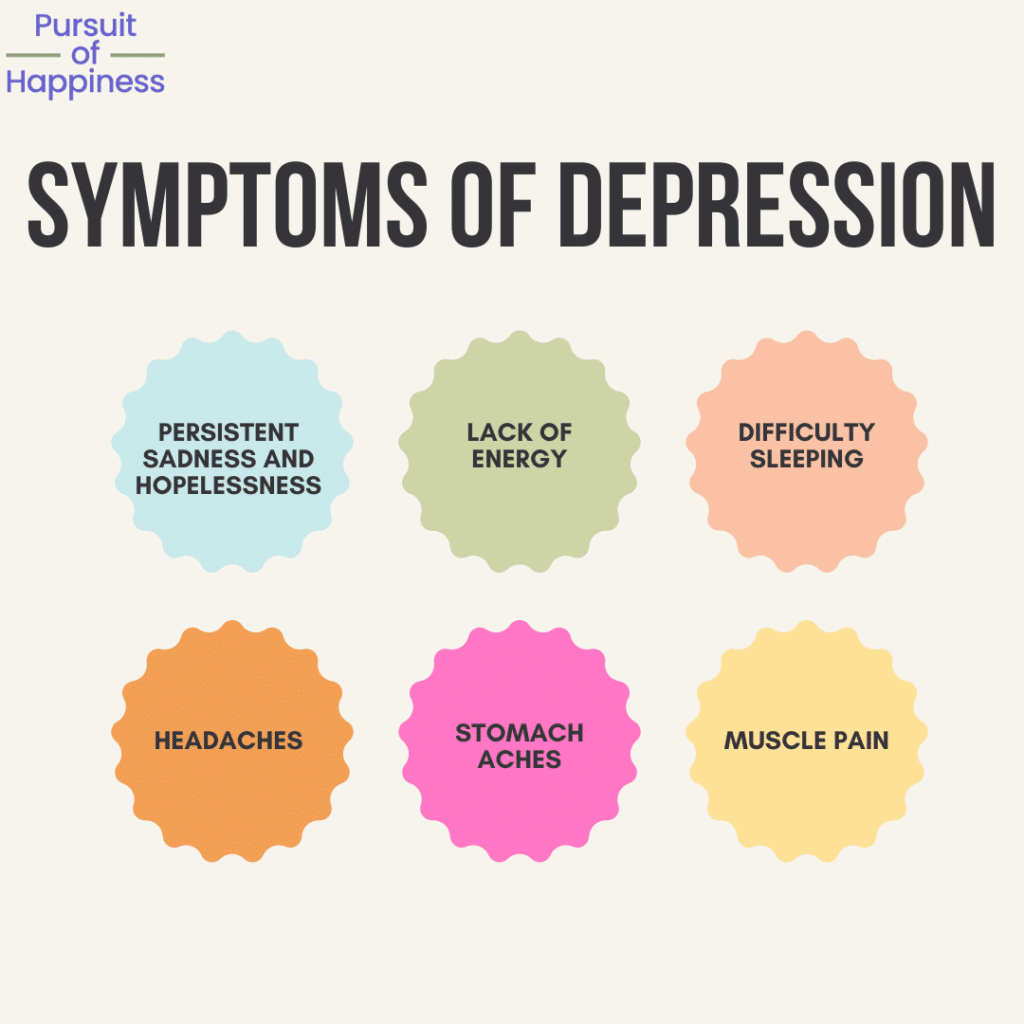
The symptoms of depression vary from person to person, with some individuals experiencing only a handful of symptoms while others may experience a range of them. Followings are the ten common symptoms of depression:
- Persistent sadness and hopelessness: If you are experiencing feelings of sadness and hopelessness that persist for more than two weeks, it may be a sign of depression.
- Loss of interest: If you are no longer interested in activities that you once enjoyed, it may be a sign of depression.
- Lack of energy: Depression can leave you feeling exhausted, even after getting plenty of rest. Note that having a lack of energy from time to time cannot be considered a sign of depression.
- Difficulty sleeping: Depression can cause lasting insomnia or make it difficult to stay asleep.
- Changes in appetite: Depression can cause a loss of appetite or lead to overeating.
- Headaches: Depression can cause frequent headaches as a symptom, which can be debilitating for those who experience them.
- Stomach aches: Depression can also cause persistent stomach aches and gastrointestinal problems, which may include vomiting, diarrhea, or constipation.
- Muscle pain: Depression can cause consistent muscle aches and tension, which can be especially noticeable in the neck, shoulders, and back.
- Difficulty concentrating: Depression can make it difficult to focus or remember things.
- Suicidal thoughts: Depression can make you feel like life is worthless and can cause suicidal thoughts. In such a case you must ask for immediate help.
Behavioral Symptoms of Depression
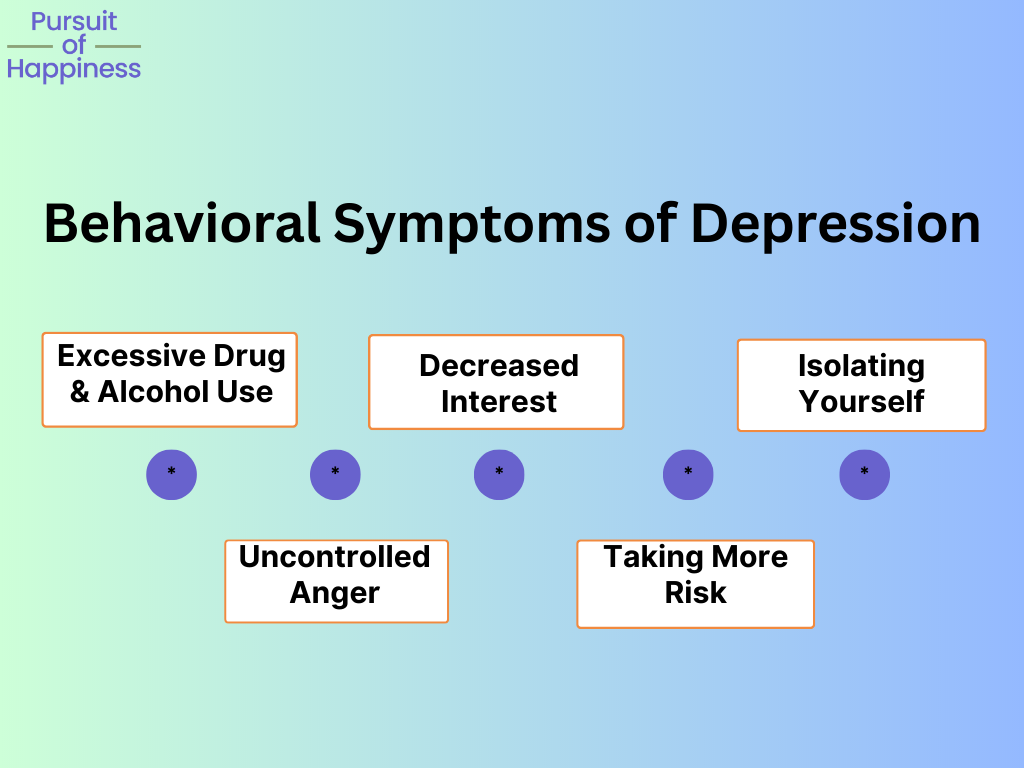
Depression can also manifest in various behavioral symptoms beyond the classic signs of fatigue and specific aches. For some individuals, depression may result in an increase in drug or alcohol use as a means of coping with their emotions. This can be particularly dangerous, as substance abuse can further exacerbate feelings of hopelessness and contribute to a worsening of symptoms.
Other behavioral symptoms may include uncontrolled anger, decreased interest in sexual activity, and a tendency to isolate oneself from others. Individuals with depression may also engage in risky activities or behaviors that put their safety at risk.
It is essential to recognize that these behavioral symptoms are not always visible to others, and individuals may go to great lengths to hide them from friends and family. This can make it even more challenging to identify and address underlying mental health issues.
Exploring Conditions that Mimic Signs of Depression
Depression can be a challenging condition to diagnose, as its symptoms can overlap with other physical and mental health conditions. It is important to consider other conditions that can mimic depression’s symptoms to ensure an accurate diagnosis and effective treatment plan.
- Hypothyroidism: It is a disorder that occurs when the thyroid gland does not produce enough hormones. Hypothyroidism can cause symptoms such as fatigue, difficulty concentrating, and changes in appetite, which can overlap with depression’s symptoms.
- Vitamin Deficiencies: Vitamin deficiencies, such as low levels of vitamin B12 or D, can also cause fatigue and a lack of energy.
- Chronic pain conditions: Conditions such as fibromyalgia, migraine or arthritis, can also mimic depression’s symptoms, as they can cause physical pain and a decrease in activity levels.
- Anxiety disorder: Anxiety or panic, can have symptoms that overlap with depression, such as irritability and difficulty sleeping.
- Stress: Tiredness, headaches, stomach aches and muscle aches can be triggered by stress.
It is also worth noting that individuals can experience multiple conditions simultaneously, which can complicate diagnosis and treatment. However, with proper evaluation and diagnosis, it is possible to develop an effective treatment plan that addresses all underlying health concerns.
Medical Depression Treatment Options
While depression can feel overwhelming, it is a treatable condition. There are several effective treatment options available, and with the right support, individuals can experience significant improvement in their symptoms and quality of life.
One of the most common treatment options for depression is therapy, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) or interpersonal therapy (IPT). Therapy can help individuals identify negative thought patterns and develop coping skills to manage depression. Additionally, therapists can work with individuals to address underlying issues that may be contributing to depression, such as unresolved trauma or relationship problems.

In some cases, medication may also be prescribed to manage depression symptoms. Antidepressant medications, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), can help regulate brain chemicals that are associated with mood regulation. It is essential to work closely with a healthcare provider to find the right medication and dosage, as each individual’s response to medication can vary.
7 Habits for Depression Prevention: Science of Happiness

Positive psychology, or the science of happiness, can be a powerful tool for individuals seeking to prevent or manage depression. By focusing on building positive emotions and experiences, individuals can cultivate a sense of resilience and well-being that can help them cope with life’s challenges. Here are seven habits that can help promote happiness and prevent depression:
- Nurture relationships: Building and nurturing close relationships with family and friends can provide a sense of belonging, social support, and love. Spend time with those who matter most to you, and make an effort to stay connected even during challenging times.
- Practice acts of kindness: Engaging in acts of kindness, whether it’s volunteering, donating to charity, or simply helping someone in need, can boost feelings of happiness and well-being. These acts can also help shift focus away from personal worries and problems.
- Take care of your body: Taking care of your body is essential for both physical and mental health. Eat a balanced diet, exercise regularly, and prioritize sleep. These habits can improve mood, reduce stress, and increase energy levels.
- Find your flow: Finding a hobby or activity that brings a sense of “flow,” or deep concentration and engagement, can provide a sense of purpose and fulfillment. Whether it’s painting, playing music, or gardening, find an activity that brings joy and focus to your life.
- Embrace spiritual engagement and find meaning: Engaging in spiritual or meaningful activities, such as meditation, yoga, or prayer, can provide a sense of connection to something larger than oneself. These practices can also help cultivate a sense of inner peace and calm.
- Know your strengths: Understanding your personal strengths and values can help you identify areas of meaning and purpose in your life. Take a strengths assessment or simply reflect on what activities bring you the most joy and fulfillment.
- Have a positive mindset: Finally, cultivating a positive mindset can help shift focus away from negative thoughts and emotions. Practice gratitude by focusing on what you are thankful for, challenge negative self-talk, and try to find the positive in challenging situations.
By incorporating these habits into daily life, individuals can help prevent or manage symptoms of depression. While these habits may not be a substitute for professional treatment, they can serve as a valuable tool for promoting well-being and happiness.
To measure your current condition regarding these 7 habits you can take our happiness quiz:
If you want to learn more about science of happiness and put it into action you can check our science of happiness courses:

Frequently Asked Questions Regarding Depression
What is depression?
Depression is a psychiatric illness that can significantly impact a person’s emotional state, cognition, and actions. It can cause persistent feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and worthlessness, leading to changes in the way a person thinks, feels, and behaves.
What are the types of depression?
When it comes to understanding mood and emotions, it’s important to differentiate between clinical depression, episodic depression, and simply feeling blue. All are experienced as depression, but they vary in intensity and their need for treatment.
- Feeling blue is a common experience characterized by temporary feelings of sadness or low mood. It is often a normal and transient response to life stressors or challenges, and it tends to resolve on its own.
- Episodic depression refers to periods of intense sadness or low mood that come and go. These episodes may be triggered by specific events or circumstances, and while they can be distressing, they tend to be time-limited and may not meet the criteria for a clinical diagnosis of depression.
- Clinical depression refers to a persistent and pervasive mental health disorder characterized by intense feelings of sadness, loss of interest, and a range of physical and emotional symptoms. It often requires professional treatment and can significantly impact daily functioning.
What causes depression?
Depression can be caused by a variety of factors, including genetics, chemical imbalances in the brain, environmental factors, and life events such as trauma, loss, or chronic stress.
How is depression treated?
Depression can be treated through medicines, therapy, and lifestyle changes or combination of them. Antidepressant medications can help balance brain chemistry, while therapy can help individuals learn coping skills and strategies for managing depression. Lifestyle changes such as exercise, healthy eating, and stress reduction can also be effective in managing symptoms of depression.
How long does depression treatment take?
The length of depression treatment can vary depending on the individual and the severity of their symptoms. In some cases, treatment may only last a few months, while in other cases it may be necessary to continue treatment for years.
How can I support a loved one with depression?
Supporting a loved one with depression can be challenging, but it is important to be patient, understanding, and supportive. Encourage your loved one to seek professional help, and offer to accompany them to appointments. Listen actively, and offer help with daily tasks or responsibilities as needed.
How is depression different from anxiety?
While depression and anxiety can share some symptoms, such as irritability and difficulty sleeping, they are distinct mental health conditions. Depression is characterized by persistent feelings of sadness and disinterest, while anxiety is characterized by persistent feelings of worry and fear. People with anxiety may also experience physical symptoms such as rapid heartbeat or sweating.
How is depression different from stress?
While stress is a normal response to challenging or demanding situations, depression is a mental health condition. Stress is often characterized by feelings of overwhelm or pressure, while depression is characterized by persistent feelings of sadness and disinterest. While stress can be managed through coping strategies such as time management or relaxation techniques, depression often requires professional treatment.