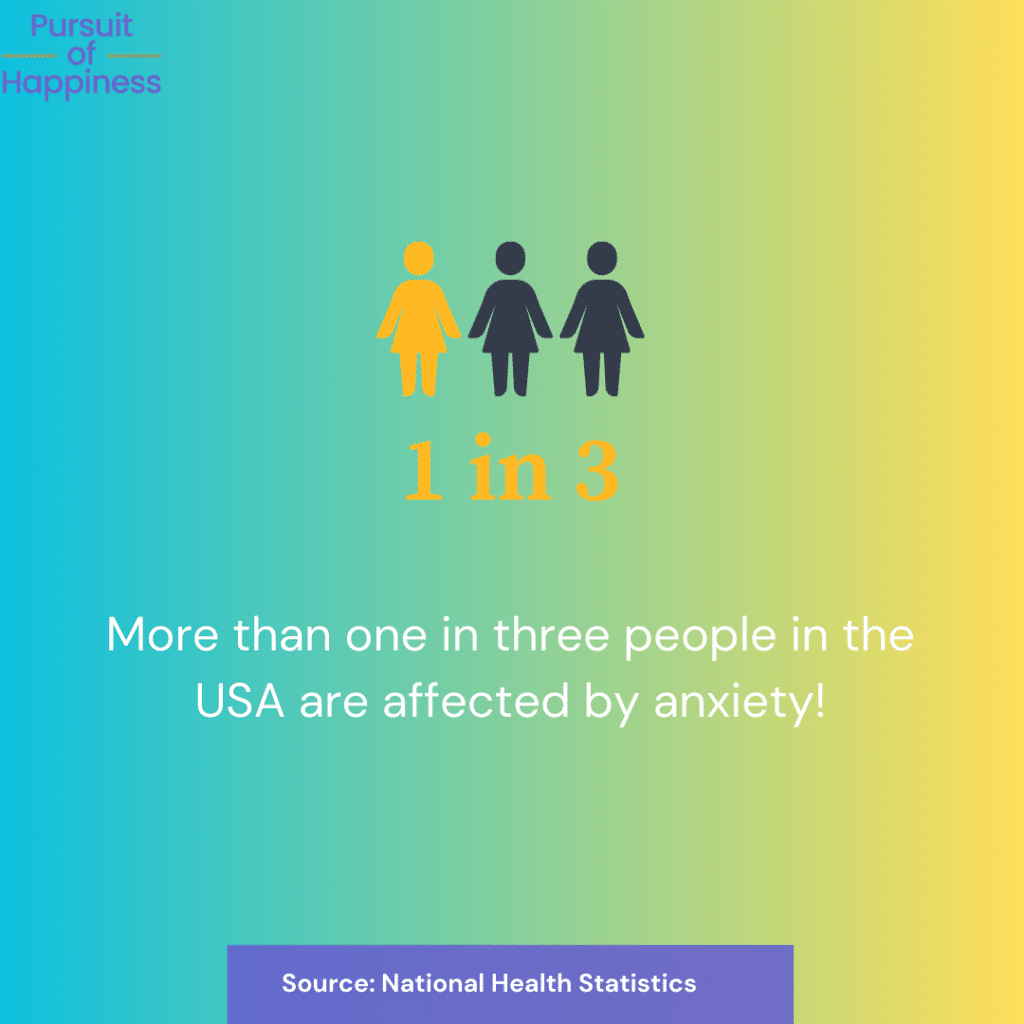
According to the National Health Statistics Report, 36.6% of adult Americans feel some degree of anxiety, where:
- 25,5% of the population were indicated as having low anxiety.
- 7% of the population were indicated as having medium anxiety.
- 4.2% of the population were indicated as having high anxiety.
While occasional feelings of worry or nervousness are a normal part of life, excessive anxiety can disrupt daily functioning and negatively impact overall well-being of:
People need to first understand the anxiety to take action against it. To assist you determine whether you have anxiety or not, we will first look at the symptoms of anxiety in this article. Then, we offer practical, scientific recommendations and best practices for reducing anxiety and boosting well-being.
Common Physical Symptoms of Anxiety

Anxiety can manifest in various physical symptoms, often resembling other medical conditions. These symptoms can include:
- Dizziness: Many individuals experience dizziness because of anxiety. It is essential to understand that anxiety-induced dizziness is usually temporary and not life-threatening.
- Fatigue and Tiredness: The constant worry can impact your energy levels. Implementing self-care practices and ensuring sufficient rest can help combat fatigue.
- Headaches: Anxiety often triggers tension headaches or migraines. Practicing relaxation techniques, getting regular exercise, and maintaining a healthy sleep routine can contribute to reducing the frequency and severity of headaches
- Diarrhea and Digestive Issues: Anxiety can disrupt the normal functioning of the digestive system, leading to diarrhea or other gastrointestinal problems. Maintaining a balanced diet and exercising regularly can help combat these symptoms.
- Stomach Pain: Anxiety can manifest as stomach pain or discomfort. Adopting healthy eating habits, reducing caffeine intake, and managing stress can contribute to alleviating these symptoms.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Anxiety can induce feelings of nausea and, in some cases, vomiting.
- Shortness of Breath: Anxiety can cause a sensation of difficulty breathing or shortness of breath. Practicing deep breathing exercises and seeking relaxation techniques can be helpful in managing this symptom.
- Chills and Body Temperature Changes: Some people may experience chills or changes in body temperature due to anxiety. These sensations are the body’s response to heightened stress levels.
- Dry Mouth: Anxiety can result in a dry mouth, often accompanied by a frequent urge to drink water. Staying hydrated and practicing relaxation techniques can help alleviate this symptom.
- Sore Throat: Anxiety-induced muscle tension can lead to a sore throat. Engaging in stress-reducing activities such as deep breathing exercises and maintaining a healthy lifestyle can aid in managing this symptom.
- Blurred Vision: Although less common, anxiety may cause temporary blurred vision.
You may experience other uncommon anxiety symptoms that we have not listed here. Additionally, not all of these anxiety symptoms must coexist for you to have anxiety. Finally, many other mental and physical illnesses’ symptoms may share similar symptoms, as we discuss in more detail below. Therefore, we advise you to consult a specialist so you may be sure whether you have anxiety or not.
Emotional and Behavioral Symptoms of Anxiety
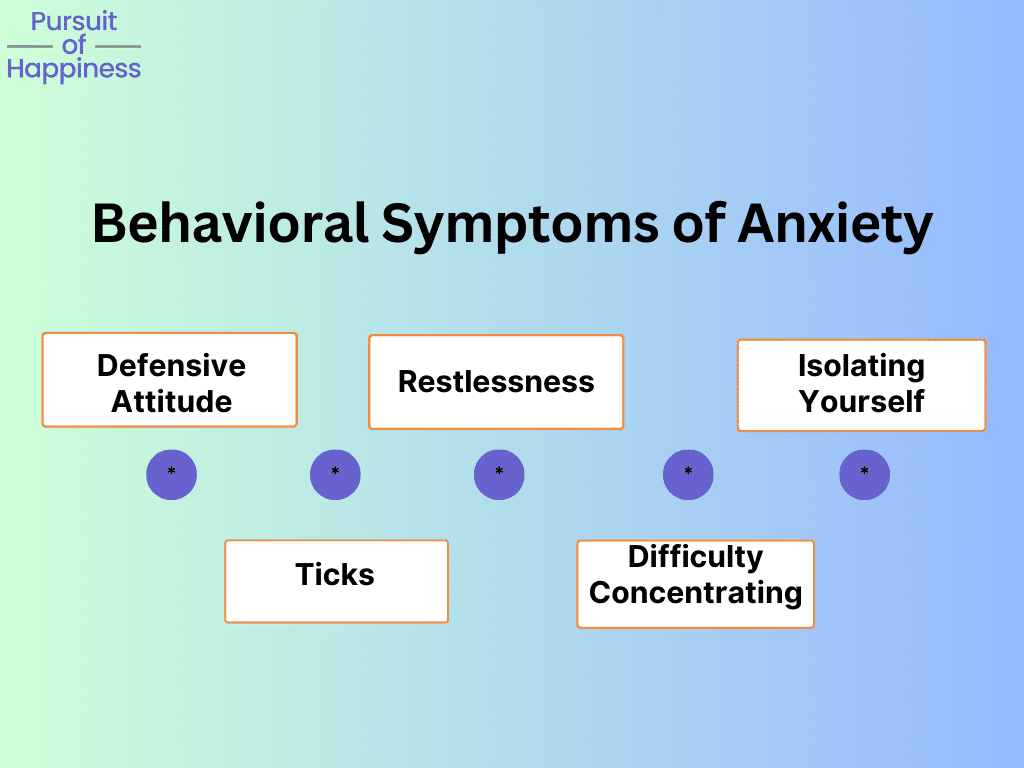
In addition to the physical symptoms mentioned earlier, anxiety can also manifest through various emotional and behavioral changes. These symptoms can significantly impact an individual’s well-being and daily life. Here are some common behavioral symptoms of anxiety:
- Defensive Attitude: Anxiety can make individuals feel constantly on edge and defensive. They may become easily irritated, have a heightened sensitivity to criticism, or feel the need to protect themselves from perceived threats. It’s important to recognize this behavior and seek healthy coping mechanisms to manage it.
- Avoidance and Isolation: Anxiety can lead individuals to avoid situations or activities that trigger their anxiety. They may withdraw from social interactions, cancel plans, or isolate themselves to reduce their perceived exposure to potential stressors. However, this avoidance can further reinforce anxiety in the long run. Gradually confronting feared situations with the support of a therapist or loved ones, and engaging in hobbies can help break this cycle.
- Restlessness and Fidgeting: Anxiety often accompanies a sense of restlessness and an inability to relax. People may display repetitive behaviors (ticks), such as tapping their fingers, bouncing their legs, or constantly shifting their position. Engaging in calming activities like deep breathing exercises, practicing mindfulness, or participating in relaxation techniques can help manage restlessness.
- Difficulty Concentrating: Anxiety can impair an individual’s ability to concentrate and focus on tasks. Racing thoughts and worries can make it challenging to stay engaged and perform at their best. Creating a structured environment, breaking tasks into smaller, manageable chunks, and employing concentration techniques, such as mindfulness or meditation, can aid in improving focus.
Investigating Conditions that Mimic Symptoms of Anxiety

While anxiety is a common mental health condition, similar symptoms can also be caused by other medical illnesses or conditions. Here are a few examples of disorders that can mimic symptoms of anxiety:
- Depression: Depression shares similar symptoms with anxiety, including fatigue, changes in sleep patterns, irritability, and difficulty concentrating. In some cases, depressive symptoms may be more prominent than anxiety symptoms. A comprehensive evaluation can help differentiate between the two and ensure appropriate treatment.
- Stress-related Disorders: Prolonged exposure to stress can lead to various stress-related disorders, such as adjustment disorder or post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). These conditions can cause symptoms like restlessness, irritability, sleep disturbances, and hypervigilance, which can overlap with anxiety. Understanding the underlying cause of your symptoms is crucial for developing an effective treatment plan.
- Other Medical Conditions: Certain medical illnesses, such as thyroid disorders, hormonal imbalances, cardiovascular problems, or neurological conditions, can mimic many anxiety symptoms such as fatigue, sleep problems, aches in different places of the body etc.
- Vitamin deficiencies: Low levels of vitamins such as B12 or vitamin D, can contribute to mood disturbances and fatigue, which may be mistaken for anxiety. A thorough medical examination can help identify any underlying medical conditions that require specific treatment.
- Substance Use or Withdrawal: The misuse of certain substances, including alcohol, drugs, or medications, can lead to anxiety-like symptoms. Similarly, withdrawal from substances can also cause intense anxiety as a temporary effect. It’s essential to disclose any substance use history to your healthcare provider to ensure accurate diagnosis and appropriate intervention.
Remember, only a healthcare professional can provide a comprehensive evaluation and diagnosis. If you are experiencing symptoms resembling anxiety, it is highly recommended to you that you consult a doctor or mental health specialist. They will conduct a thorough assessment, taking into account your medical history, symptoms, and any relevant factors, to determine the accurate diagnosis and develop an individualized treatment plan.
Medical Anxiety Treatment Options

Here are some common medical treatment options for anxiety:
- Medications: In some cases, doctors may prescribe medications to manage anxiety symptoms. These medications may include selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), benzodiazepines, or beta-blockers. Medications can help regulate brain chemistry, alleviate symptoms, and provide short-term relief. However, they should only be used under the guidance and supervision of a healthcare professional due to potential side effects and the need for careful monitoring.
- Therapy: Psychotherapy, also known as talk therapy, is a widely used and effective treatment approach for anxiety. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is often recommended as a first-line therapy for anxiety disorders. It focuses on identifying and challenging negative thought patterns and behaviors associated with anxiety. Other forms of therapy, such as exposure therapy, dialectical behavior therapy (DBT), or acceptance and commitment therapy (ACT), may also be utilized depending on individual needs.
7 Habits for Anxiety Prevention: The Science of Happiness

Developing healthy habits can play a crucial role in preventing anxiety and promoting overall well-being. By incorporating science-backed strategies into our daily lives, we can cultivate resilience and create a foundation for happiness. Here are seven habits that can help prevent anxiety:
- Acts of Kindness: Engaging in acts of kindness towards others not only benefits them but also boosts our own well-being. Acts of kindness, whether small or large, promote feelings of connection, gratitude, and purpose, all of which contribute to reducing anxiety.
- Physical Well-being: Prioritizing physical well-being is essential for managing anxiety. Taking care of our bodies through proper nutrition, regular exercise, and quality sleep can have a significant impact on mental health. Incorporate a balanced diet, engage in physical activity you enjoy, and establish a sleep routine that allows for sufficient rest.
- Flow: Experiencing a state of “flow” occurs when we become fully absorbed in an activity that challenges and interests us. This could be pursuing a hobby, engaging in creative work, or participating in sports. Flow promotes a sense of purpose, accomplishment, and contentment, which can help alleviate anxiety and promote overall well-being.
- Spiritual Engagement and Meaning: Nurturing our spiritual well-being can provide a sense of purpose, connection, and inner peace. Engaging in activities that align with our values, such as meditation, prayer, or spending time in nature, can foster a deeper sense of meaning and reduce anxiety. Explore practices that resonate with you and incorporate them into your daily life.
- Signature Strengths and Virtues: Identifying and leveraging our unique strengths and virtues can boost self-confidence and resilience. Reflect on your inherent qualities and talents and find ways to utilize them in your personal and professional life.
- Positive Mindset: Cultivating a positive mindset involves consciously shifting our focus toward gratitude, optimism, and self-compassion. Practice gratitude by regularly acknowledging the things you appreciate in life. Challenge negative thoughts and replace them with more positive and realistic perspectives. Treat yourself with kindness and self-acceptance, recognizing that nobody is perfect.
- Social Connections: Nurturing healthy social connections is vital for overall well-being and anxiety prevention. Surround yourself with supportive and positive relationships. Seek opportunities to connect with others, engage in meaningful conversations, and participate in activities that foster social bonds. Building a strong support network contributes to resilience and reduces the impact of anxiety.
Remember, habits are formed through consistent practice and repetition. Start by incorporating one or two habits into your daily routine, and gradually expand from there.
To find out how you are currently performing regarding these 7 habits you can take our science based happiness quiz:
To learn more about science of happiness and positive psychology and put your learnings into action you can check our science of happiness courses:

Frequently Asked Questions About Anxiety
What is anxiety?
Anxiety is a normal human response to stress or perceived threats. It involves feelings of:
- Fear
- Worry
- And unease.
Anxiety is often accompanied by the physical symptoms we mentioned above. While occasional anxiety is common, excessive and persistent anxiety may indicate an anxiety disorder.
What are the types of anxiety?
What causes anxiety?
Anxiety can be caused by a combination of factors, including:
- Genetic factors
- Brain chemistry imbalances (both genetic, environmental and eating-drinking habits can play a role on it)
- Traumatic experiences such as tragic accidents
- Ongoing stress.
Each individual’s experience of anxiety may have unique causes and triggers. Pursuit of Happiness emphasizes that while genetic and environmental components of anxiety may be difficult, or even impossible, to change, individuals have significant control over their habits, making them a crucial factor in anxiety prevention.
What is the relationship between anxiety and panic attacks?
In some cases, chronic anxiety can trigger panic attacks. Panic attacks can occur as a result of an overwhelming sense of anxiety, leading to a sudden surge of intense fear and physical symptoms.
How long does anxiety treatment take?
While some individuals may experience significant improvement within a few months, others may require longer-term management and support. The duration of anxiety treatment mostly depends on the severity of your condition.
How is anxiety different from stress?
Stress is a response to specific external pressures or demands, while anxiety often involves a sense of worry or unease without an immediate or identifiable trigger. While stress tends to be temporary, anxiety may persist even when the stressor is removed.
How is anxiety different from depression?
Anxiety is characterized by excessive worry and fear, while depression involves persistent feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and a loss of interest or pleasure in daily activities. However, both anxiety and depression can have overlapping symptoms and they can coexist.
How can you support a loved one with anxiety?

- Educate yourself about anxiety to better understand their experience.
- Be patient and non-judgmental.
- Learn their triggers and help create a supportive environment that promotes their well-being.
- Offer practical help, such as accompanying them to therapy sessions or engaging in stress-reducing activities together like yoga.
- Encourage self-care practices and healthy coping mechanisms.
Remember our happiness courses can assist you in supporting your loved ones with coping with anxiety.